Source: AgriLife Today | June 30, 2020
Since the release of information about Asian giant hornets, Texas A&M AgriLife entomologists are being inundated with cicada killers and other lookalike insects submitted for identification as a possible “murder hornet,” which thus far has only been found in Washington state in the U.S.

While the agency wants to continue to encourage Texans to be vigilant in watching for the Asian giant hornet, they also want to help provide guidance that will help narrow the focus.
David Ragsdale, Ph.D., chief scientific officer and associate director of Texas A&M AgriLife Research, and professor in the Department of Entomology, said many photos of Texas native cicada killers, or ground hornets, are being submitted as suspected Asian giant hornets. He said their website receives five to 10 photos a day, and agency pest management agents and specialists around the state have also been handling inquiries.
It’s a bird, it’s a plane … it’s a cicada killer
In May, the concern about Asian giant hornet was enough to prompt Gov. Greg Abbott to request a task force be mobilized to prepare Texas against the Asian giant hornet’s arrival.
But June is the normal month for the cicada killer wasp, a common large wasp in Texas, to start showing up and this prompted posts on Facebook and in news feeds mistakenly reporting cicada killer wasps as sightings of the Asian giant hornet.

“Most everyone has seen the cicada killer wasp that is very large, but has mostly been ignored in the past,” Ragsdale said. “With the most recent news of the Asian giant hornet, they are now paying attention to the native Texas insect.”
While some people thought they had been seeing the newly pictured murder hornets for years, AgriLife Extension experts want to clarify, “No, you haven’t.” Now they are providing outlets to help tell the difference between the Asian giant hornet and similar looking pests.
Holly Davis, Ph.D., Texas A&M AgriLife Extension Service entomologist in Weslaco, and Pat Porter, Ph.D., AgriLife Extension entomologist in Lubbock, recently developed a short video explaining the differences between the “murder hornet” and several common lookalikes here in Texas.
“To date, we have identified hundreds of insects that people in Texas suspect might be Asian giant hornets (murder hornets),” Porter said. “Eighty percent of these have been either the eastern cicada killer or western cicada killer. It is understandable how non-entomologists would have trouble deciding which was which.”
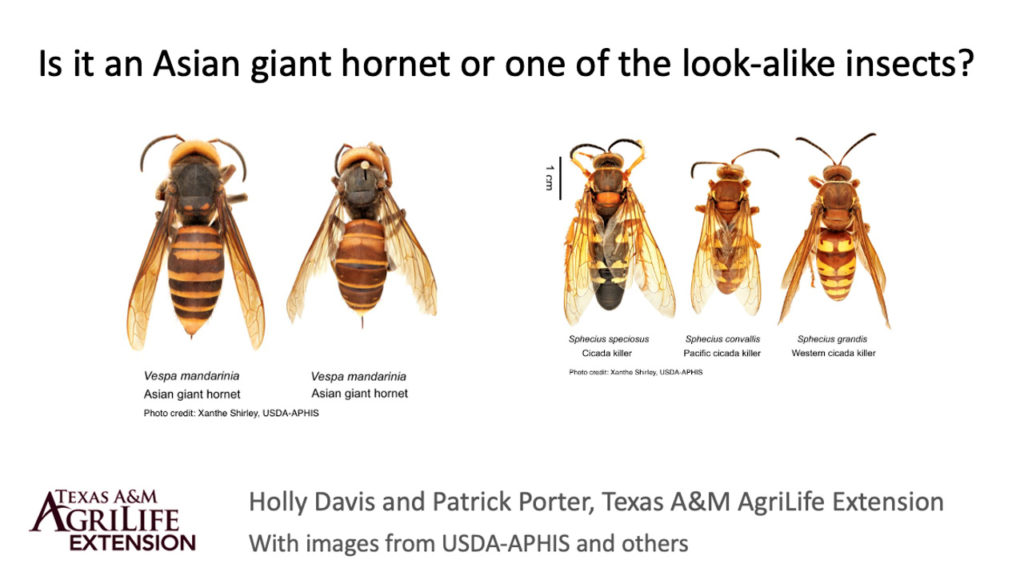
How to tell the difference
“First, the Asian giant hornet is native to Japan and South Korea, and it has only been found in parts of British Columbia, Canada and the northwestern corner of Washington state,” Davis said. “There have been no confirmed reports of these hornets in other U.S. locations, including Texas.”
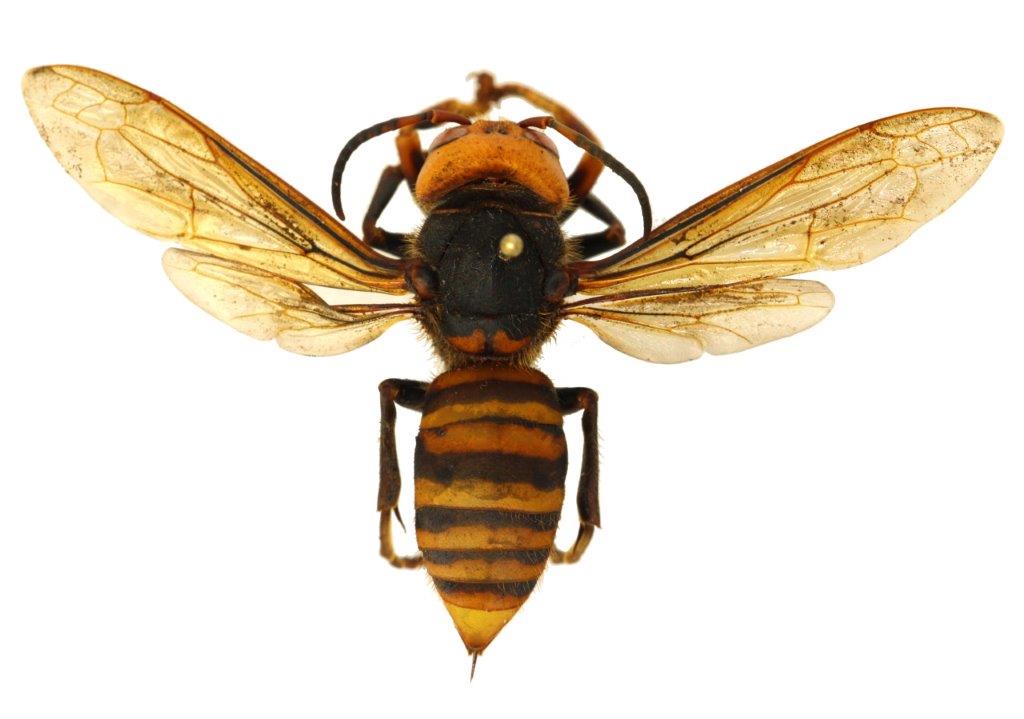
There are a number of Texas native species of wasp, hornet, yellow jacket and bees, but what really separates Asian giant hornet and a few of our native species is their size. The ones most likely to be confused with Asian giant hornet are three species of cicada killers and the pigeon horntail.
The Asian giant hornet is the world’s largest known hornet measuring 1.5-2 inches in length. It has a head as wide as its shoulders, where the wings and legs are located, or wider, and it is a bright orange or yellow. The thorax, or shoulder portion where the wings and legs are connected, is a dark brown, as are the antenna. It has a much smaller or pinched waist and then smooth looking brown and orange stripes cover the abdomen.
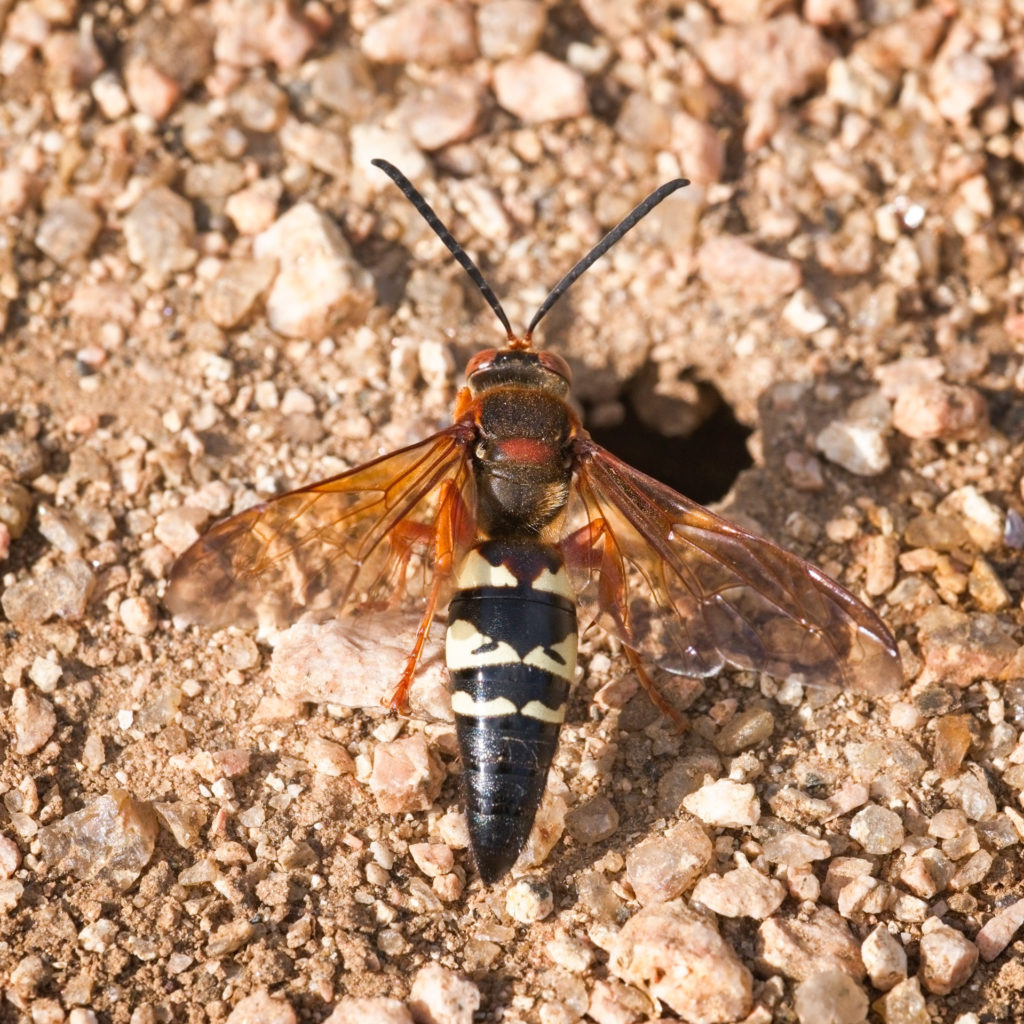
The cicada killers, of which there are three different species here in Texas, are also quite large, measuring 1-1.5 inches in length. But they will all typically have a head that is narrower than the thorax. The head and the thorax are typically the same color, a darker orange or brown color. It does also have a pinched waist. But the stripes on the abdomen will be jagged and sometimes look like mountains.
The eastern cicada killer tends to be black and yellow. The western cicada killer is closer in color to the Asian giant hornet, being reddish brown and yellow. But there is no contrasting color between the head and thorax and the stripes are jagged on the western cicada killer.
The other group of insects that are most commonly confused with the Asian giant hornet are the horntail or wood wasps. They are large, have a distinct head that is as wide or wider than the thorax, and may share the same coloration as the Asian giant hornet. However, there is one trait that is easy to spot that is different, and that is the waist. Horntails lack any appearance of a waist.
Harmful or just alarming
The Asian giant hornet preys on bees and can decimate local honey bee populations, essential for most fruit and vegetable crop production. The Asian giant hornets also are fiercely protective of their nests and will deploy painful stings that can cause fatal allergic reactions in people already sensitive to bee stings.
The cicada killer and wood wasps, however, are solitary and thus do not aggressively protect their nesting sites by attacking in large numbers, Davis said. Cicada killers, however, may cause alarm due to the males’ territorial behavior, dive-bombing or buzzing people and animals that walk into their territory.
“Although cicada killers are solitary, you can often find numerous individuals in areas with sandy soils where females dig nests in the ground,” she said. “These nests appear as dime to quarter sized holes. As females come and go, provisioning their nest with cicadas they paralyze with a sting and carry back to their nests.
“The males are more interested in mating. Thus, they may try to chase off intruders they perceive as a threat to their mating opportunities. However, male wasps are not capable of stinging, thus they are not dangerous, just a nuisance for a few weeks out of the year during the nesting season. Females can sting but are not aggressive and reports of stings are rare.”
Horntails and wood wasps may have what appear to be very long stingers, but they are unable to sting. They lack venom glands and instead they use this structure, called an ovipositor, to insert eggs into plant tissue, hence the name wood wasp, Davis said.
