
This Week’s Drought Summary
This U.S. Drought Monitor (USDM) week saw continued improvements on the map across areas of the South, including Texas, in response to another round of localized heavy rainfall during the past week. Overall, the recent rainfall in Texas throughout the past month has started to make a significant dent in the state’s drought conditions in some areas. In contrast, drought conditions intensified in areas of the central and northern Plains with additional degradations on this week’s map. In these areas, recent drought impact reports submitted to the National Drought Mitigation Center indicated drought-related impacts within the agricultural sector including reduced crop yields as well as deteriorating pasture and rangeland conditions. Out West, the big story of the past week has been the heat wave that has impacted the region with record-setting temperatures and critical fire-weather conditions. The hot temperatures and strong winds exacerbated conditions on the Mill Fire, which broke out in Northern California on Friday, forcing the evacuation of the town of Weed, California as well as neighboring communities. In Death Valley, California, high temperatures exceeded 125 deg F multiple times during the past week including on September 1st when the high temperature reached 127 deg F―potentially breaking the record for the hottest temperature ever recorded during September, according to preliminary reports. Elsewhere, shower activity in the Northeast led to isolated improvements in drought-affected areas of Massachusetts and Connecticut, while further to the south conditions deteriorated on the map in Delaware. In the Midwest, short-term precipitation deficits and declining soil moisture levels led to the expansion of areas of drought in northern Missouri and central Illinois.
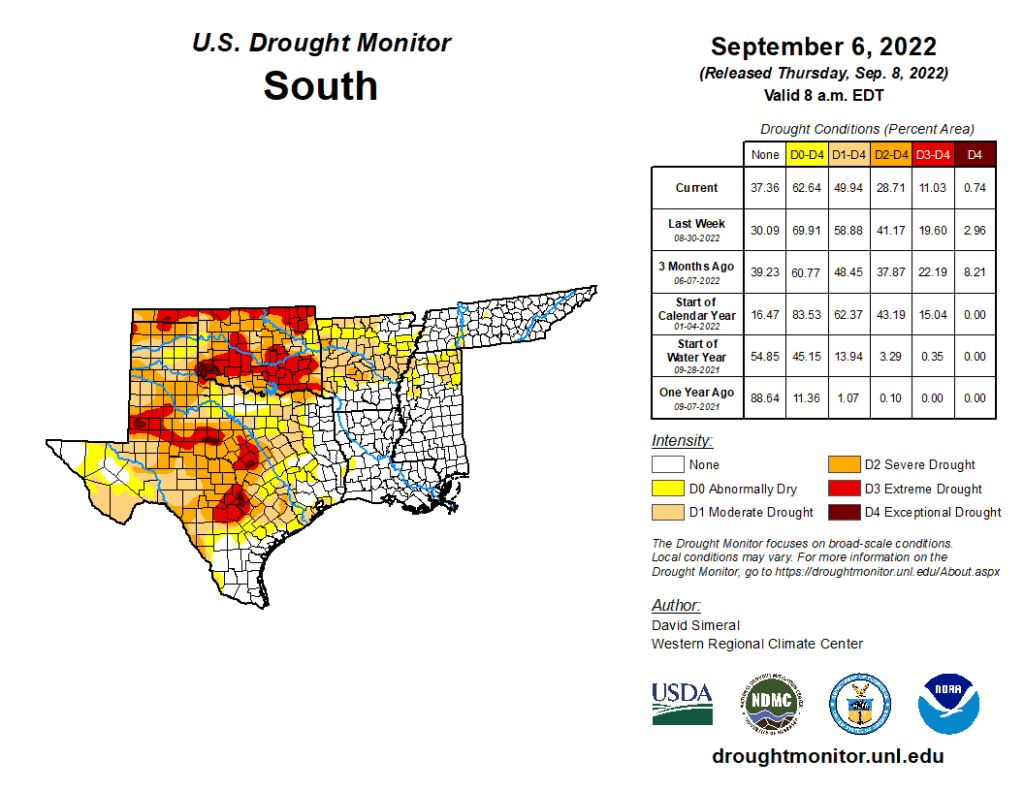
South
In the South, widespread improvements were made across Texas this week in response to another round of moderate-to-heavy rainfall that impacted isolated areas of the state, with accumulations ranging from 2 to 6+ inches. The recent rains have provided a much-needed boost to soil moisture and streamflow levels. Despite the recent rains, streamflow levels in some areas of the Hill Country have yet to recover, with gaging stations on numerous rivers and creeks reporting below-normal flows (ranging from the 2nd to the 24th percentile), according to the U.S. Geological Survey. Elsewhere in the region, this week’s rainfall led to improvements in eastern Oklahoma, northern Arkansas, northern Mississippi, and western portions of Tennessee. For the past 30-day period, much of the region experienced above-normal precipitation with the greatest positive departures (ranging from 6 to 12+ inches) observed in the Basin and Range and southern portion of the Gulf Coastal Plains of Texas, northern Louisiana, and central Mississippi. Overall, average temperatures for the week were within a few degrees of normal, with larger negative departures (2 to 4 deg F below normal) observed in western Texas.
