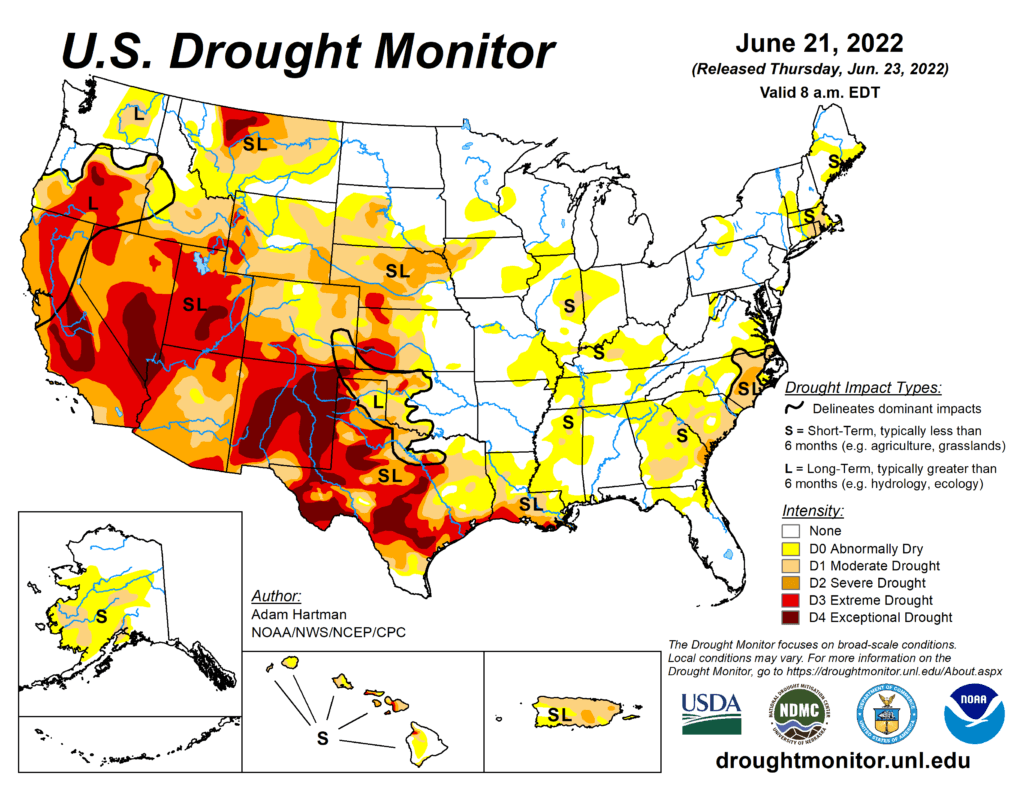
This Week’s Drought Summary
Much above-normal temperatures plagued much of the central and eastern contiguous U.S. (CONUS) this week from the Great Plains eastward to the Mississippi Valley and Southeast. The western third of CONUS, the Northeast, and coastal Mid-Atlantic experienced seasonal to below-normal temperatures. Precipitation was lacking in many locations that experienced excessive (in some cases record) heat, leading to widespread expansion of abnormal dryness and moderate drought conditions along the Mississippi and Ohio Valleys, the Southern Plains, and the Southeast. From the Central Plains northward, despite the excessive heat (daytime high temperatures above 100°F several days this week), recent improvements driven by an active storm track leading up to this week resulted in modest, more targeted degradations in the drought depiction. Another week of heavy rainfall warranted improvements in Montana. In the Pacific Northwest, below-normal temperatures and recent improvements from an active weather pattern leading up to this week resulted in improvements in some of the long-term drought indicators. Heavy rainfall associated with the Southwest Monsoon also fell across parts of the Four Corners region. However, this only acted to halt any further degradations this week. Given drought is strongly entrenched in the Four Corners, an active Southwest Monsoon circulation will need to persist for conditions to improve.
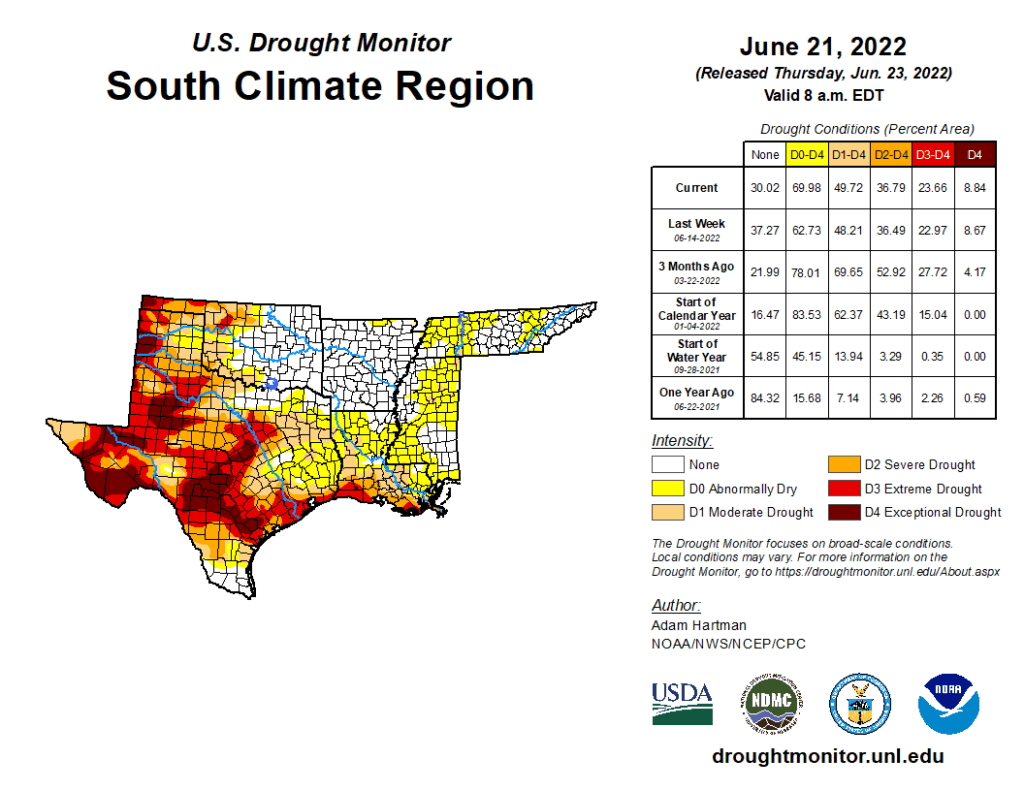
South
Extreme heat, high winds, and below-normal precipitation continued in Texas, leading to another round of degradations this week across the state. Extreme heat and below-normal precipitation also lead to the widespread expansion and addition of abnormal dryness (D0) and moderate drought (D1) across the Lower Mississippi and Tennessee Valleys. Soil moisture conditions quickly deteriorated this week (falling below the 30th percentile across many areas that saw expansion). Additionally, daily and 7-day average USGS stream flows fell below-normal (below the 24th percentile) and vegetation indices are also indicating increased stress to plants. Short-term (30 to 60-day) deficits are starting to accumulate also, with many areas across the Lower Mississippi and Tennessee Valleys experiencing 4 to 6 inch rainfall deficits over the last 60 days.
