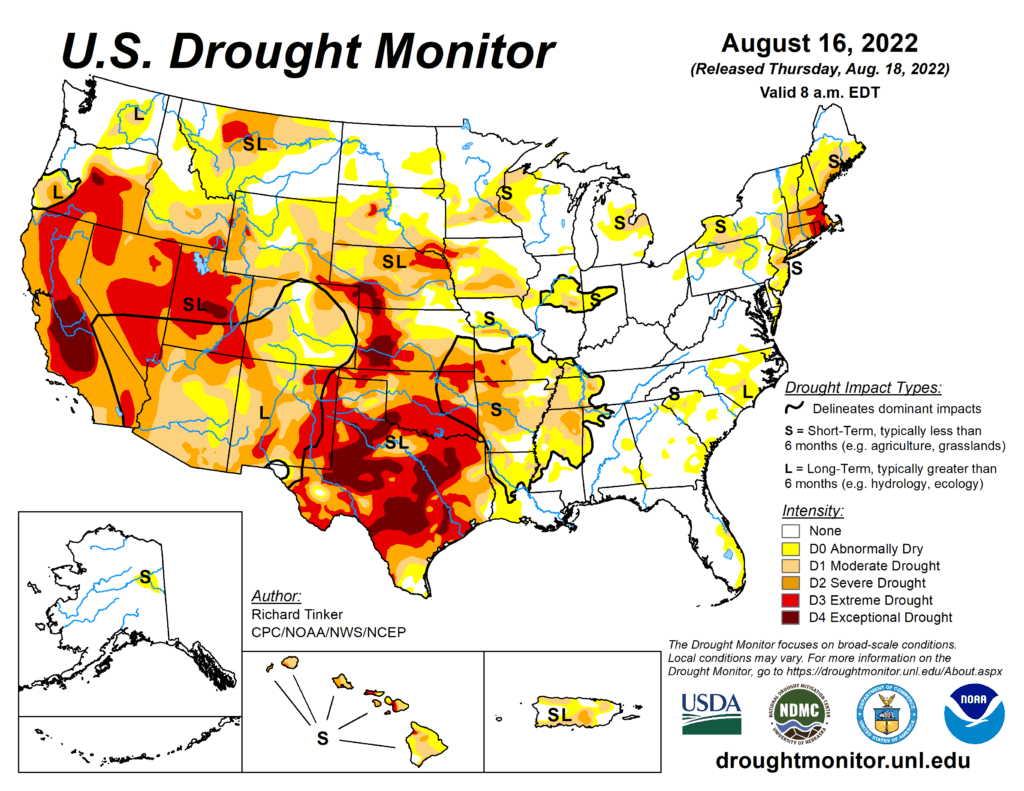
This Week’s Drought Summary
Precipitation again varied widely across the Lower 48 this week, which is not unusual during the summer. Across the interior West, monsoon rains were not as intense as last week, but remained heavier than normal. Several times the normal amount soaked most areas in the western half of the Four Corners Region, much of Nevada, southeastern California, reaching as far north as southeastern Oregon and Wyoming. Other areas receiving widespread heavy rains (and thus some improvement from recent dryness) included Deep South Texas and northwestern Nebraska. Parts of Deep South Texas recorded over 10 inches of rain, and 2 to 3 inches were common across northwestern Nebraska. Elsewhere, relatively narrow swaths of moderate to heavy rain dampened parts of the middle Mississippi Valley, Upper Midwest, and Great Lakes Region. Meanwhile, a broken pattern of moderate to heavy rain covered roughly the southeastern quarter of the contiguous 48 states. The higher amounts were in the 2 to 3 inch range though some small, highly-isolated areas recorded a bit more. In contrast, light precipitation at best fell on the Northeast, which teamed with abnormally high temperatures to induce significant and widespread intensification. Other areas observing light rain at best included part of the Upper Midwest, the north-central and south-central Plains. Conditions were seasonably dry along the West Coast.
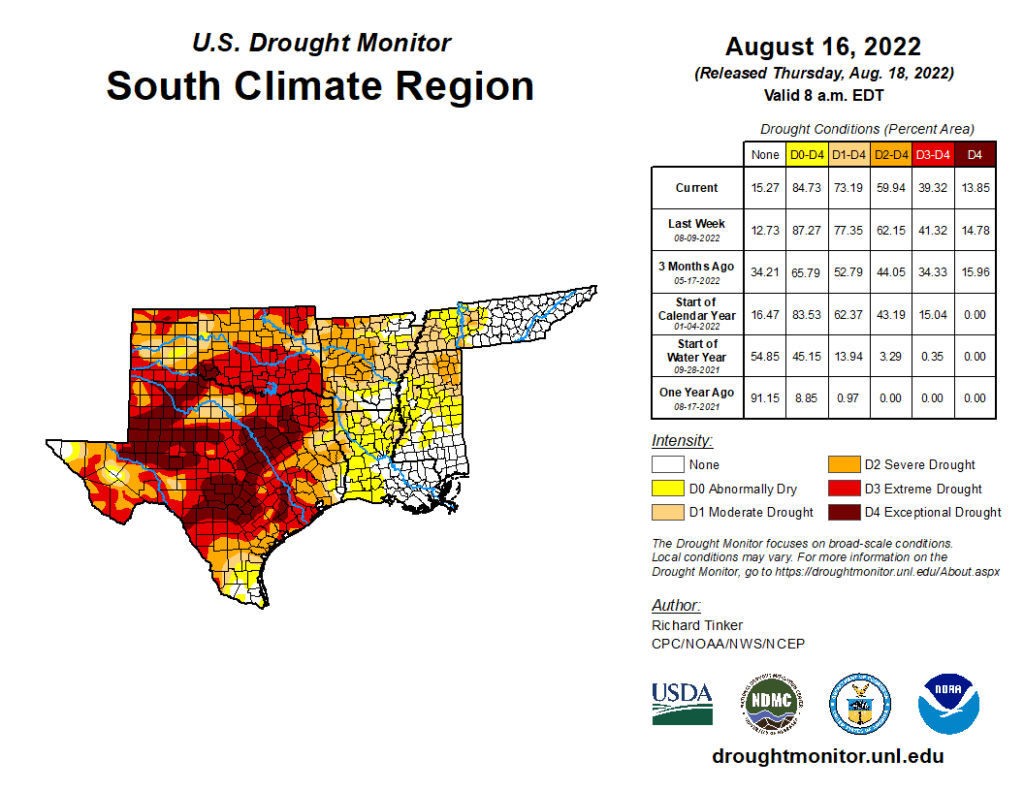
South
Last week’s precipitation – though variable – followed the same general pattern as the precious week. Heavy rains drenched much of the eastern reaches of the Region while lesser amounts and localized deterioration were noted farther west. On significant exception was Deep South Texas, where heavy to intense rainfall brought significant improvement to areas of abnormal dryness and drought. Amounts exceeding 2 inches were widespread south of a line from Webb and LaSalle Counties eastward through San Patricio County, and amounts of 5 to locally over 10 inches drenched areas north of the Mexican border counties. This prompted nearly universal 1-category improvements on the Drought Monitor, with small areas of 2-category improvement where rainfall was heaviest. Extreme drought (D2) or worse are now confined to areas north and west of Duvall County. Elsewhere, increasing rainfall brought additional improvement to the Lower Mississippi Valley and Tennessee, but amounts were generally below-normal from central Texas northward through Oklahoma. Enough rain fell on central and northern Texas to keep areas of deterioration small, but little rain fell from the Red River (South) into northern Oklahoma, where larger areas of intensification were observed. Broad areas of exceptional drought (D4) still cover much of a large area from the southern Texas Panhandle southeastward toward the Gulf Coast. Over the last half-year, rainfall deficits of 8 inches to locally over a foot have affected areas of central Texas near and south of Dallas/Ft. Worth to the Gulf Coast.
