Derrell S. Peel, Oklahoma State University Extension Livestock Marketing Specialist
Memorial Day is perhaps the biggest hamburger grilling day of the year, possibly rivaled by Independence Day. Ground beef demand has continued strong for the past twelve months after rising sharply in the second quarter of 2021 (indicated by the prices in the figure below). The ground beef market is large and complex with two major demand channels in retail grocery and food service. These market channels utilize different and largely separate supply chains that depend on a wide variety of lean and fat sources. Clark (2019) provides a more detailed account of the ground beef market, which is summarized below.
Ground beef at retail grocery typically depends almost exclusively on domestic sources of fresh beef, often marketing ground beef from specific primal sources such as ground chuck, ground round or ground sirloin. Retail grocery ground beef utilizes fatty trimmings from fed steers and heifers as well as lean beef from cow and bull slaughter, all frequently primal specific, and may include whole muscle grinds. Retail grocery frequently includes a wide range of lean to fat ground beef products ranging from 70 percent lean (the minimum to be called ground beef) to over 90 percent lean.
Food service ground beef uses a wider range of lean and fat sources. In Quick Service Restaurants (QSR), in particular, margins are extremely narrow and specialized grinders monitor a wide range of ground beef sources to control the price of ground beef within the specifications of each restaurant customer. Each restaurant chain specifies one or more lean to fat formulations, with the exact lean to fat ratio proprietary to each company. Food service ground beef will include a wide range of fresh and frozen beef trimmings from domestic as well as (mostly frozen) imported lean beef trimmings.
The ground beef market plays a critical role to balance supply and demand for the vast array of products produced by the beef industry. While the trimmings are always utilized in ground beef or other processed products, whole muscle cuts may move into or out of ground beef formulations as the supply as well as the demand for those products as muscle cuts fluctuates. Chuck products may enter ground beef grinds if they are cheap enough but increased export demand for these products, particularly in Asian markets, have reduced the use of chuck muscles in hamburger grinds. Beef products from the round are leaner and may be used to provide the additional lean needed for ground beef, but compete with higher value uses of these products, especially for processed products such as jerky.
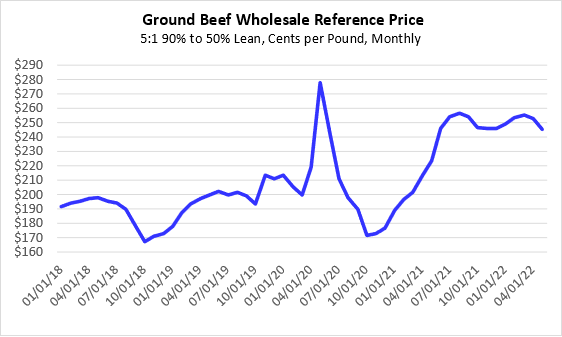
Fed steers and heifers produce significant amounts of fatty trimmings, which require additional pounds of lean product to make ground beef. For example, one pound of 50 percent lean trimmings, mixed with five pounds of 90 percent lean trimmings, will produce six pounds of 83.3 percent lean ground beef. While there are many ground beef formulations and many product mixes to achieve them, this 5:1 ratio of 90 percent lean to 50 percent lean trimmings is representative of the ground beef market. The figure below shows the wholesale price for this combination of 90s and 50s for the past several years. Strong demand for the past year has kept the wholesale price of ground beef near record levels, exceeded only by the brief spike that occurred in the initial stages of the pandemic in 2020 and a few months of reduced supply in 2014/2015.
